Michele Pietragalla , Letizia Vannucchi , Luca Carmignani , Andrea Pagliari , Claudia Calabresi, Giuseppe Alabiso , Silvia Rossi , Anna Talina Neri , Michele Trezzi , Massimo Di Pietro
SOC Radiodiagnostica Ospedale San Jacopo Pistoia
Reparto Malattie Infettive Ospedale San Jacopo Pistoia
83-year-old male patient admitted to the ED with cough and fever (39°C) for three days. Prior medical history: DM type 2, HTA, ex heavy-smoker.
pO2 95%, no leukopaenia, slight increase of CPR, LDH transaminase levels.
Chest ultrasound: bilateral interstitial engagement, basal consolidations with air broncogram and pleural effusion.
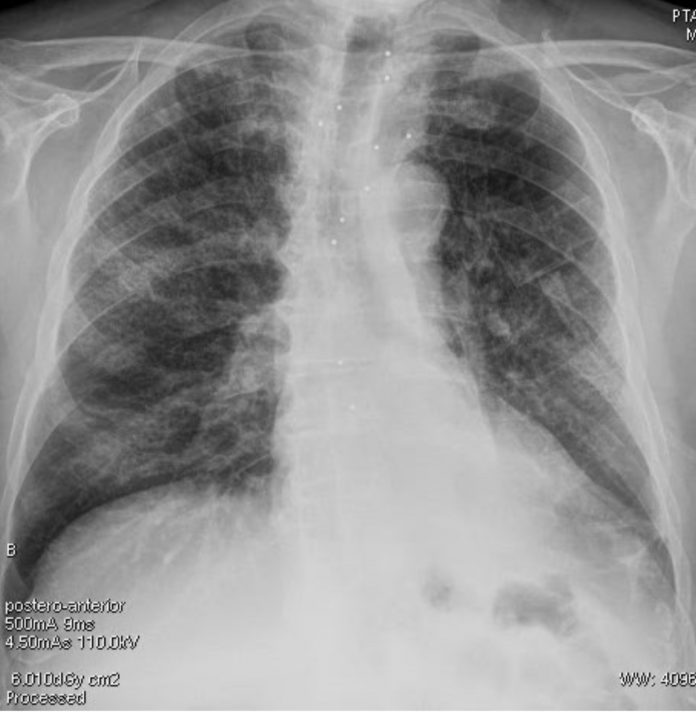
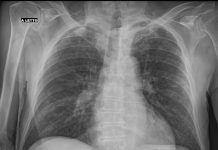
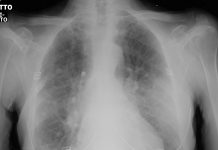
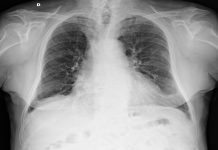
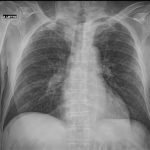
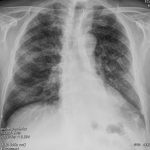
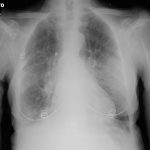
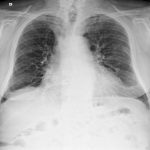
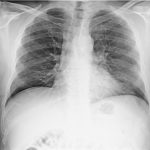
Chest radiography (supine):

bilateral pulmonary “ground-glass” opacities.
CT


Multiple and diffuse “ground-glass” opacities, predominantly in the mantellar regions of the lungs, with initial consolidations and “crazy paving” patterns.
RT-PCR was positive for SAR-CoV-2.
After 3 days of hospitalization, D-dimero was measured as a screening for Tolicizumab therapy, with very high values (17234 micrograms/ml). At the same time, the patient showed respiratory failure.
A CTA was performed for suspected pulmonary embolism.

Filling defects of segmental and subsegmental arteries of the lower lobes.
COVID patients have higher risk for pulmonary embolism:
Chen, Jianpu and Wang, Xiang and Zhang, Shutong and Liu, Bin and Wu, Xiaoqing and Wang, Yanfang and Wang, Xiaoqi and Yang, Ming and Sun, Jianqing and Xie, Yuanliang. Findings of Acute Pulmonary Embolism in COVID-19 Patients (3/1/2020). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3548771.